
Stethoscopes are a fundamental medical instrument for healthcare professionals to diagnose and monitor patients. While we have a range of machines for analysing patient signs and symptoms, understanding how, where, and what to listen for can drastically change clinical indications for diagnosing conditions. In Australia, nurses’ roles in patient care have expanded significantly, indicating a notable shift towards increased stethoscope use among nursing professionals and an expectation of proficiency.
This shift has led to a more collaborative approach in healthcare delivery, allowing for more practitioners to contribute to diagnosing and managing patient conditions. As a result, healthcare teams can address the needs of a larger patient population, enhancing overall access to care and improving health outcomes across communities. By equipping nurses with essential diagnostic tools, the healthcare system in Australia is better positioned to meet the growing demands of an ageing population and an increasingly complex healthcare landscape.
Benefits of Proficiency with Stethoscope Use
For healthcare professionals, being adept with a stethoscope offers numerous advantages:
- Early Detection of Conditions: Proficient use allows for the early identification of heart, Lung, and vascular diseases, leading to timely interventions.
- Enhanced Patient Assessment: Understanding how to interpret various sounds can help professionals conduct thorough assessments, ensuring no critical details are overlooked.
- Improved Communication: Proficiency fosters better communication between healthcare providers and patients. Professionals can explain findings clearly and informally.
- Increased Confidence: Mastery of stethoscope use builds confidence in diagnosing and managing patient conditions, which is crucial in high-stress environments.
- Versatility Across Disciplines: Whether a nurse, physician, or allied health professional, proficiency with a stethoscope is a foundational skill that enhances overall clinical competence.
How Stethoscopes Work
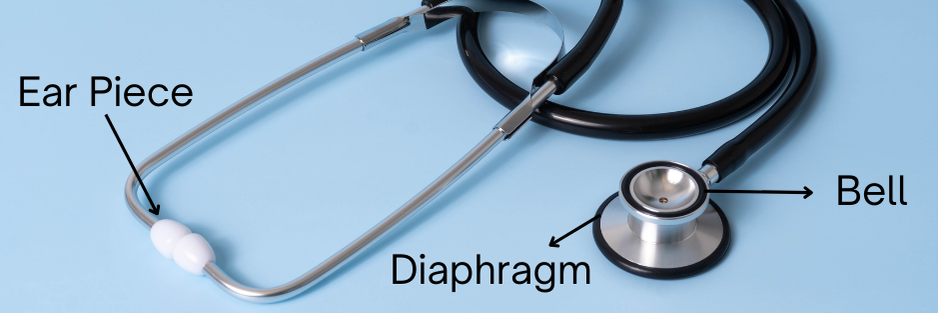
At its core, a stethoscope amplifies internal bodily sounds, allowing healthcare providers to hear and interpret them. The device consists of several key components:
- Chest Piece: This is the part that comes in contact with the patient’s body. It typically has two sides: a diaphragm and a bell.
- Diaphragm: This flat, circular part is sensitive to high-frequency sounds, making it ideal for detecting heartbeats, breath sounds, and normal bowel sounds. It vibrates when pressed against the skin, transmitting sound waves through the tubing.
- Bell: The bell is a smaller, concave part that captures low-frequency sounds, such as certain heart murmurs and vascular sounds. It works best when gently placed on the skin.
- Tubing: This flexible conduit transmits sound from the chest piece to the healthcare provider’s ears. The length and material of the tubing can affect sound quality.
- Earpieces: These fit snugly in the ears and help block out external noise, allowing the user to focus on the sounds from the body.
How Sounds Are Amplified
When a healthcare professional places the diaphragm or bell against the patient, vibrations produced by internal sounds (like the heart beating or air moving in and out of the lungs) travel through the tubing. The earpieces then allow the provider to hear these sounds clearly, enabling them to assess the patient’s condition.
Uses of Each Side of the Stethoscope
Diaphragm
The diaphragm is designed to capture high-frequency sounds. Here are its primary uses:
- Heart Sounds: Detecting regular heartbeats, murmurs, and gallops.
- Lung Sounds: Evaluating breath sounds for conditions like wheezing, crackles, or diminished airflow.
- Bowel Sounds: In gastrointestinal assessments, listen for normal, hyperactive, or absent bowel sounds.
Bell
The bell is best for low-frequency sounds. Its uses include:
- Heart Murmurs: Identifying subtle murmurs that may indicate valve issues.
- Vascular Sounds: Assessing bruits in arteries, which can signal conditions like atherosclerosis (atherosclerosis is the buildup of fats, cholesterol and other substances in and on the artery walls).
- Certain Lung Sounds: Capturing specific low-frequency respiratory sounds that may indicate pathology.
Stethoscopes remain invaluable in the healthcare industry, enabling professionals to listen to and interpret bodily sounds effectively. By understanding the function of each side of the stethoscope and honing their skills, healthcare providers can greatly improve their diagnostic capabilities, ultimately leading to better patient outcomes. As such, continuous training and practice with this essential instrument should be a priority for all health professionals.
